
SUSTAINABILITY:
What It Means, Why It Matters, and How to Get Started
Why Sustainability Matters More Than Ever
From rising landfill costs to complex regulatory compliance, poor waste management can quickly turn into a financial, operational, and reputational risk. But when approached strategically, sustainability becomes a competitive advantage—helping your organization stay compliant, operate more efficiently, and showcase positive environmental practices to your stakeholders.
At Certified Waste Solutions, we partner with clients to simplify sustainability. Whether you manage dozens of properties or oversee a complex facility, we help you reduce waste at the source, improve recycling outcomes, and track progress with data you can confidently use. This page will walk you through the foundations of sustainability, how it connects to waste management, and what you can do—right now—to make meaningful, measurable progress.
Rethinking Sustainability
Contrary to popular belief, the concept of sustainability is about more than just being “green.” By definition, sustainability is the practice of meeting today’s needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. It’s a mindset that asks: Are the decisions we’re making right now setting us up for long-term success, or are they short-term fixes that come with long-term costs? To be sustainable, you must make more thoughtful decisions today that protect your business and our shared future.
For businesses, that means rethinking the systems we rely on—how we manage waste, choose and use resources, and create value. It’s about shifting away from surface-level solutions and embracing strategies that build resilience, drive efficiency, and that protect both the planet and your bottom line.
Not sure where to start?
Chat with our VP of Sustainability to get practical answers and ideas.

Leslie Brooks, VP of Sustainability
The Three Pillars of Sustainability
Environmental Pillar
When we think about sustainability, the environment is often the first thing that comes to mind—and for good reason. The environmental pillar is about making choices today that reduce harm and extend the life of the resources we rely on. For businesses, that could mean finding smarter ways to handle waste, reduce pollution, or rethink how materials are sourced and disposed of.
Some common strategies include:
Landfill Diversion – Recycling, composting, and reusing materials to reduce environmental impact and conserve resources
Renewable Energy – Switching to solar, wind, or geothermal to reduce reliance on fossil fuels
Conservation Efforts – Protecting land, water, and biodiversity to ensure long-term ecosystem health
For property and facility managers, this pillar reinforces the value of proactive, sustainable operations—ones that not only meet regulations but also protect the future of your business and community.


Economic Pillar
The economic pillar focuses on building systems that are efficient, resilient, and cost-effective over the long term. This pillar ensures that actions are financially viable and contribute to economic development without depleting future resources. It asks questions like: Is this investment cost-effective in the long run? Will it support jobs, innovation, and growth? Can we avoid short-term gains that lead to long-term losses?
Key components of economic sustainability include:
Green Business Practices – Reducing resource consumption, making environmentally preferred purchases, and reducing waste
Sustainable Development – Designing buildings, infrastructure, and systems with long-term impacts in mind
Investment in People – Creating jobs, supporting innovation, and driving sustainable economic growth
True economic sustainability redefines prosperity, certifying that industries and economies grow without compromising environmental health or social equity. Whether you’re overseeing a facility or an entire property portfolio, the economic pillar reminds us that responsible choices often lead to better performance—and fewer surprises down the line.
Social Pillar
The Social Pillar is about creating fair, equitable communities where everyone’s needs are heard and met. It promotes harmony within societies by addressing issues like inequality, access to resources, and social injustices. Social sustainability requires us to think beyond our individual communities and consider the well-being of the global population; it is the most challenging needle to move and required for progress.
Examples include:
Fair Trade and Ethical Labor – Ensuring that workers across the supply chain are treated fairly
Community Development – Supporting access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure in underserved areas
Equity in Access – Making sure everyone—regardless of background—has access to clean water, safe housing, and essential services
For busy professionals focused on keeping things running, this pillar offers a reminder: the systems you manage have the power to uplift the people they serve. Thoughtful choices today can lead to stronger, more resilient communities tomorrow.

The pillars of sustainability aren’t separate checkboxes—they’re interconnected and most effective when used together to inform responsible, forward-thinking decisions.
.jpg)
Addressing Symptoms vs. Causes
In sustainability—and especially in waste management—it’s easy to focus on what’s immediately visible: rising costs, overflowing bins, or increasing regulatory pressure. But real progress requires us to go deeper and solve problems at the source, not simply treat the symptoms.
A clear example of addressing symptoms vs. causes in waste management lies in how we respond to the issue of overflowing landfills:
Addressing the symptom involves building more landfills or expanding existing ones to accommodate growing waste volumes. This temporarily solves the space problem but doesn't stop the root issue—excessive waste generation.
Addressing the cause involves implementing strategies to reduce waste at the source. This can include redesigning products for durability and recyclability, encouraging reusable packaging, and promoting consumer behavior changes. This approach targets the core problem, which is our throwaway culture and inefficient consumption patterns.
When we shift the focus from reaction to prevention, we make waste systems smarter and more cost-effective. It's not just about managing waste—it’s about rethinking how and why that waste is created in the first place. This kind of thinking leads to better outcomes across the board: to long-lasting, systemic solutions that support sustainability and paves the way to systems thinking.
Systems Thinking
Sustainability challenges rarely exist in isolation. They’re part of a larger system—interconnected with operations, supply chains, budgets, and human behavior. That’s where systems thinking comes in.
Instead of addressing one problem at a time, systems thinking looks at the bigger picture: how each part of a process affects the others. It’s about understanding relationships, anticipating ripple effects, and designing lasting solutions.
Let’s break it down with a common example in supply chain management:
Say your company wants to reduce its environmental impact by switching to biodegradable packaging. Employing systems thinking means taking a few extra steps to make sure the change actually works.
Sourcing: Is the new material truly sustainable, or does it require more water and energy to produce?
Operations: Will the new packaging run through existing equipment, or will it require costly adjustments?
Transportation: Is it heavier or bulkier, increasing emissions and shipping costs?
End-of-life Consideration: Will consumers know how to compost or recycle it properly, and do they have access to the right infrastructure?
By zooming out, the company can make smarter choices that balance environmental goals with operational efficiency and customer usability.
This approach applies just as well to waste management. A change may seem small, but it can affect labor costs, hauling frequency, tenant behavior, and even lease renewal rates. Systems thinking helps you anticipate those impacts and design programs that are genuinely sustainable—not just in name.
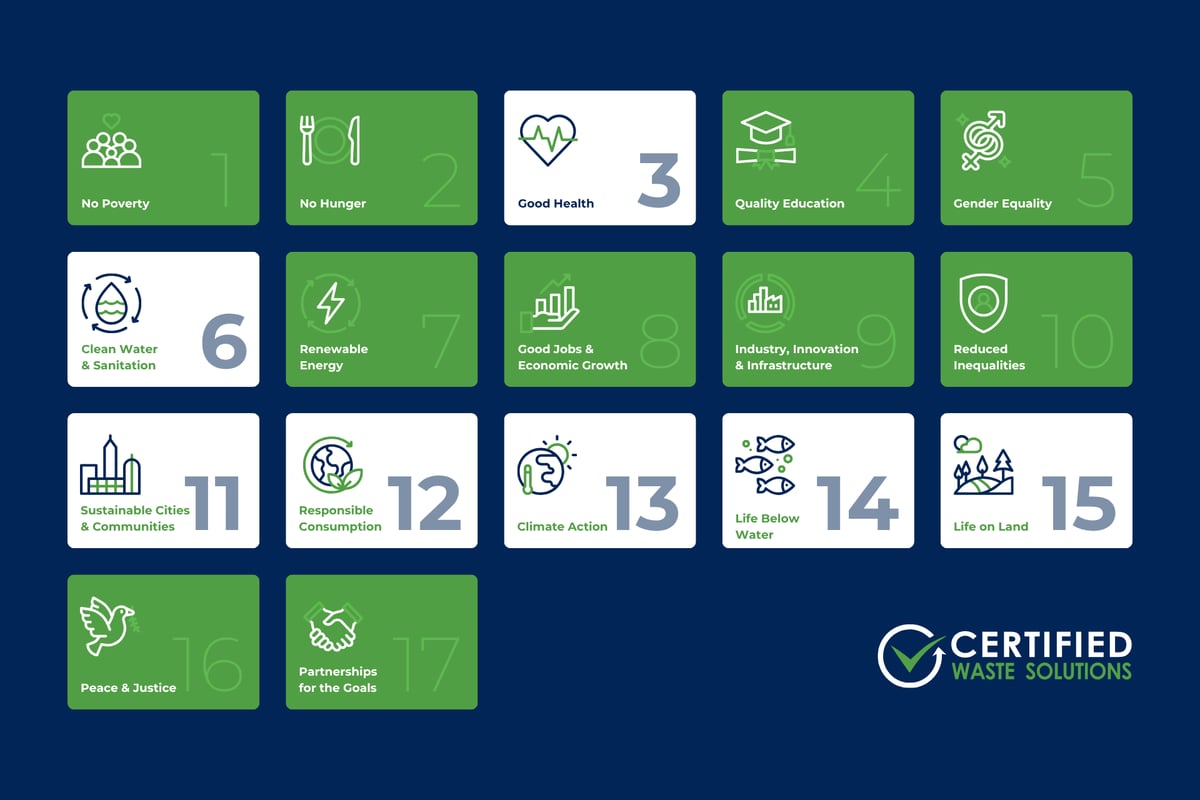
Waste Management & the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
What Are the Sustainable Development Goals?
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are 17 global targets established by the United Nations to address the world’s most pressing challenges—everything from clean energy and responsible production to public health and poverty reduction. These goals were created to provide a clear, shared roadmap for building a better, more sustainable future. For businesses, they help guide smart decisions that align with long-term success, compliance, and resilience.
Waste management is vital in achieving several SDGs, which are closely tied to environmental health, public well-being, and long-term resource stewardship.
Where waste management and sustainability intersect
When most people think about sustainability, they picture things like renewable energy or electric vehicles. But waste management is one of the most immediate, tangible ways to make a real impact, both environmentally and operationally.
Why? Because how we handle waste affects everything from climate to water quality. Improper use of disposal methods—like landfilling, open dumping, or incineration—can lead to pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and ecosystem damage. On the other hand, when we exercise more sustainable practices like recycling, composting, and source reduction we help minimize harm by:
- Conserving resources and promoting more efficient processes
- Increasing resilience and reducing long-term costs
- Enhancing social responsibility and creating cleaner, safer spaces for employees, customers, and communities
For businesses and property managers, this is where sustainability becomes practical. Even small changes—like cutting down on single-use items or adding better signage—can create ripple effects that benefit your entire organization.
Here are the most directly impacted goals:
Good Health and Well-Being (SDG 3): Poorly managed waste increases the risk of disease transmission—particularly in vulnerable communities. Effective waste systems help reduce health hazards and create safer environments.
Clean Water and Sanitation (SDG 6): Improper disposal can contaminate water supplies and disrupt sanitation infrastructure. Sustainable waste practices protect water quality and support healthier ecosystems.
Sustainable Cities and Communities (SDG 11): Thoughtful waste management is essential for reducing urban pollution, improving sanitation, and making cities cleaner, safer, and more resilient.
Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12): At the heart of waste management, this goal promotes reducing waste through prevention, reuse, recycling, and smarter resource use—key components of a circular economy.
Climate Action (SDG 13): Landfills and open burning release methane and other harmful emissions. Reducing waste at the source and improving diversion rates helps mitigate climate change.
Life on Land (SDG 15): Safe handling and disposal of waste prevent soil degradation and protect ecosystems—preserving biodiversity and supporting healthier land use.
Sustainability Strategy and Reporting
What Is ESG?
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) is a framework that organizations use to measure and report their sustainability efforts. For most businesses, waste management falls squarely within the Environmental pillar. The way you handle materials—how much you generate, how much you divert from landfill, and how you report those actions—can significantly impact your performance, compliance, and reputation.
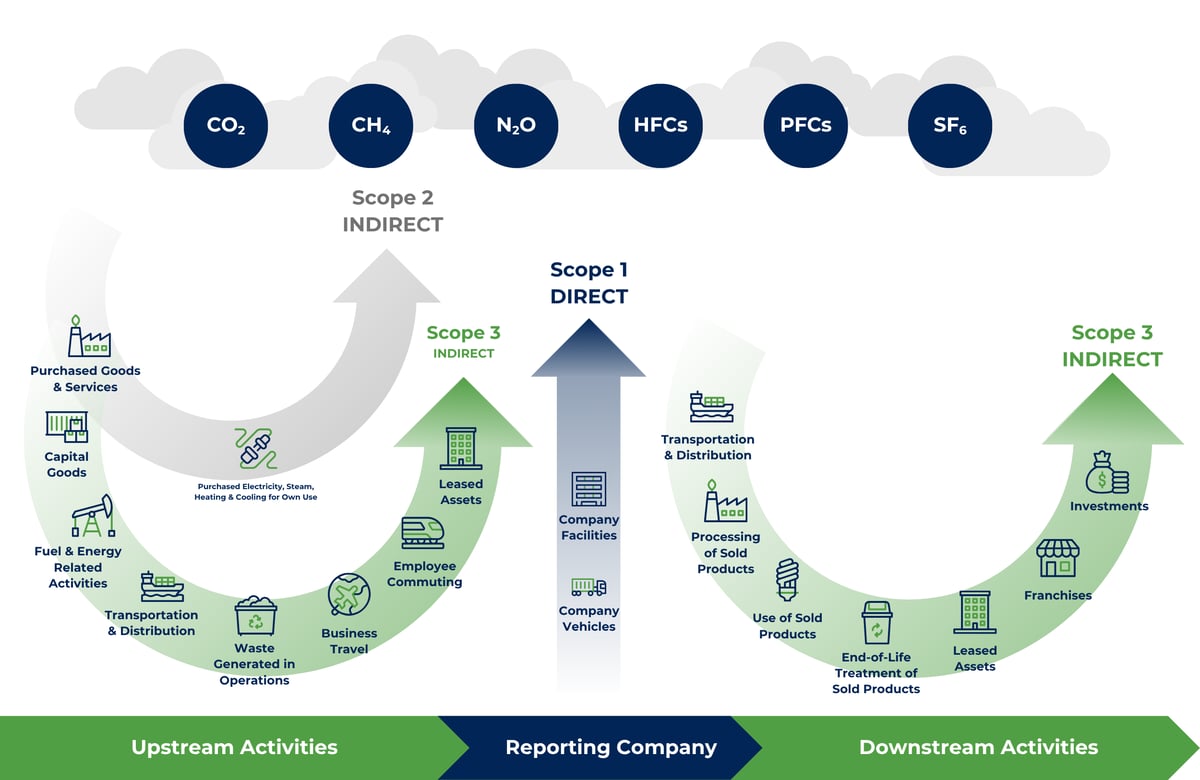
What Are Scope 3 Emissions?
When organizations talk about reducing their carbon footprint, they assess three emission categories—Scope 1, 2, and 3. Scope 1 includes emissions from company-owned/controlled sources (direct emissions), whereas Scope 2 focuses on emissions from purchased electricity (indirect emissions). Then we have Scope 3, which is often considered the most challenging to quantify. This includes everything from the goods and services your company purchases to the end-of-life treatment of the products that are sold. This scope reflects the quality of an organization's waste management practices and material/operation efficiency.
While Scope 3 emissions are classified as "indirect," they are a direct consequence of a company's choices about how it handles waste from its operations. Decisions around sourcing, packaging, equipment, and discarded materials all play a significant role in shaping these emissions. The good news? These impacts can, in fact, be measured, managed, and reduced through intentional, smarter planning.
Why Scope 3 Waste Emissions Matter
- They can make up a large share of your total carbon footprint
- They directly connect to diversion, zero-waste, and ESG goals
- They impact your ability to meet compliance standards or build toward certifications
- They offer a chance to improve both sustainability outcomes and operational efficiency
What Sustainability Metrics to Track (and Why)
Effective waste reporting starts with a few key metrics:
- Total Waste Generated: Track how much material is leaving your site—and break it down by type (landfill, recyclables, compost, hazardous).
- Diversion Rate: This core metric tells you how much material you have kept from being landfilled.
To calculate: Diversion Rate = (Recycled + Composted + Reused) ÷ Total Waste Generated - Hazardous or Regulated Waste: Keep detailed records on any waste that requires special handling or permits.
- Emissions from Disposal or Hauling: This includes transportation-related emissions
Tracking these numbers over time gives you a clearer picture of what’s working—and where to improve.
How Reporting Supports Real Environmental Progress
Clear, consistent reporting helps turn your sustainability goals into measurable results. Whether you’re just getting started or refining an existing program, the goal is to build a reporting process that is:
- Accurate: You’re not over or underestimating your impact
- Transparent: Stakeholders know your data can be trusted
- Actionable: The insights guide decisions
Accurate reporting protects your brand from greenwashing, strengthens regulatory trust, and creates momentum across your organization. You don’t have to start big—but starting with consistency makes all the difference.
How Your Business Contributes to Meaningful Change
You don’t need to be a global corporation to make a difference. Every business, no matter the size or industry, can play a role in building a more sustainable future.
When businesses take steps to improve their waste management practices, they contribute significantly to sustainability. Every piece of waste that is reduced, reused, or properly recycled helps conserve natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize pollution.
By implementing strategies like composting organic materials, reducing single-use plastics, or partnering with managed waste service providers, companies can lessen their environmental footprint while also promoting a circular economy. Even small actions—like switching to digital documentation, improving waste sorting in the workplace, or encouraging staff to bring reusable containers—can lead to meaningful change over time.
When multiplied across departments, locations, or entire industries, these micro-efforts create momentum that drives broader transformation. They inspire employees, influence customer behavior, and set new standards for what responsible business looks like. These efforts not only align with sustainability goals but also demonstrate leadership, accountability, and a commitment to long-term environmental stewardship.
In sustainability, consistency and intent matter just as much as scale. Small, smart choices add up—and when businesses lead by example, they empower others to follow. And you don’t have to do it alone. With the right tools, partners, and strategy, sustainability becomes a natural extension of your business, not an extra burden.
Are you ready to make your business more sustainable?
Reach out to Certified Waste Solutions to talk through your current challenges and future goals—or download our Green Guide to get actionable ideas you can start using today.
Let's Talk!
We are located in
-
 CORPORATE
CORPORATE
333 S. Anita Drive, Suite 600, Orange, CA, 92868
 (714) 635-2181
(714) 635-2181
-
 ANAHEIM
ANAHEIM
555 South Rose Street, Anaheim, CA, 92805
 (714) 635-2181
(714) 635-2181
-
 NAPA
NAPA
100 Dodd Court, American Canyon, CA, 94503
 (707) 647-3700
(707) 647-3700
-
 SAN DIEGO
SAN DIEGO
3833 Bancroft Drive, Spring Valley, CA 91977
 (619) 462-0098
(619) 462-0098
.png?width=320&height=80&name=CERTIFIED%20Waste%20Solutions%20Logo%20Vector%20NO%20Tagline%20(4).png)